From Abyssal Darkness to Blinding Glare: A Benchmark on Extreme Exposure Correction in Real World
TL;DR: This paper introduces Real-world Extreme Exposure Dataset (REED) to improve extreme exposure correction in real world scenarios. The method is based on burst capturing with a range of exposures and accurate SIFT-based image alignment. The paper also introduces a method (CLIER) for extreme exposure correction based on luminance normalization, semantic awareness, diffusion, and iterative refinement. The experiments validate the efficacy of the proposed method.

Abstract
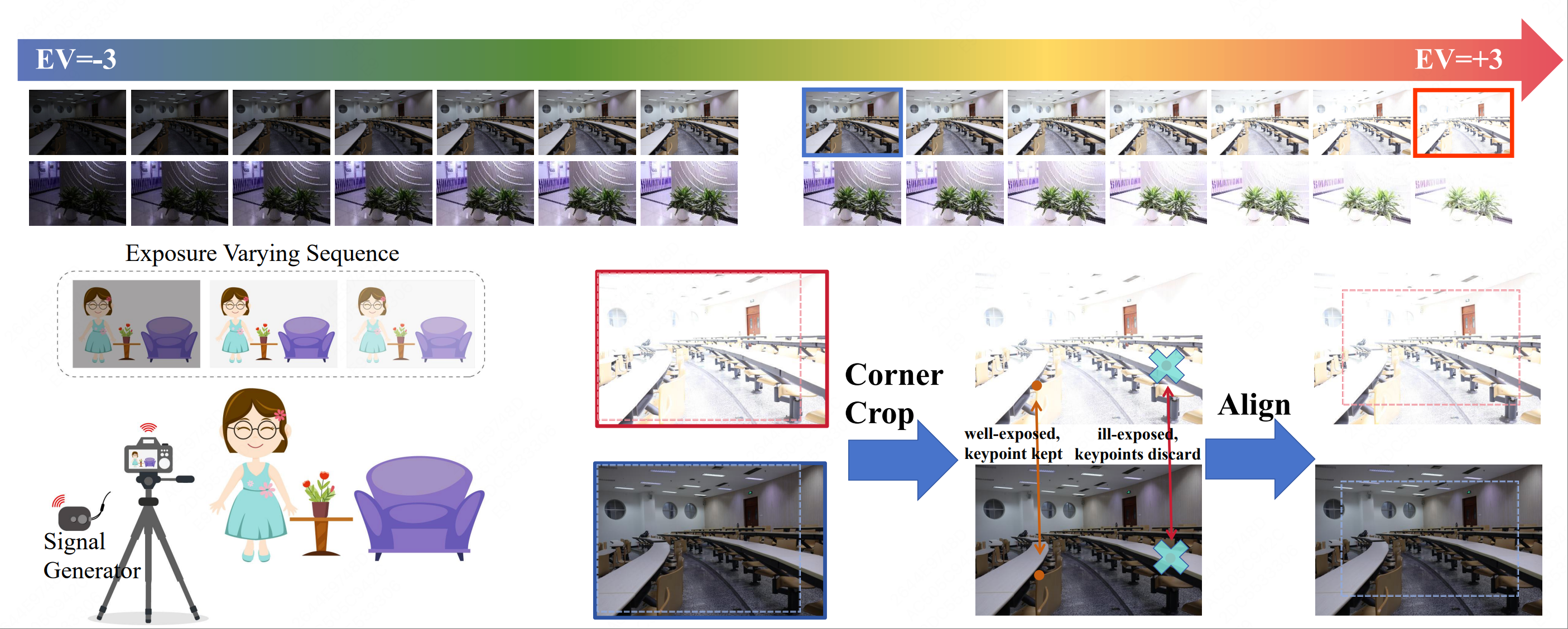
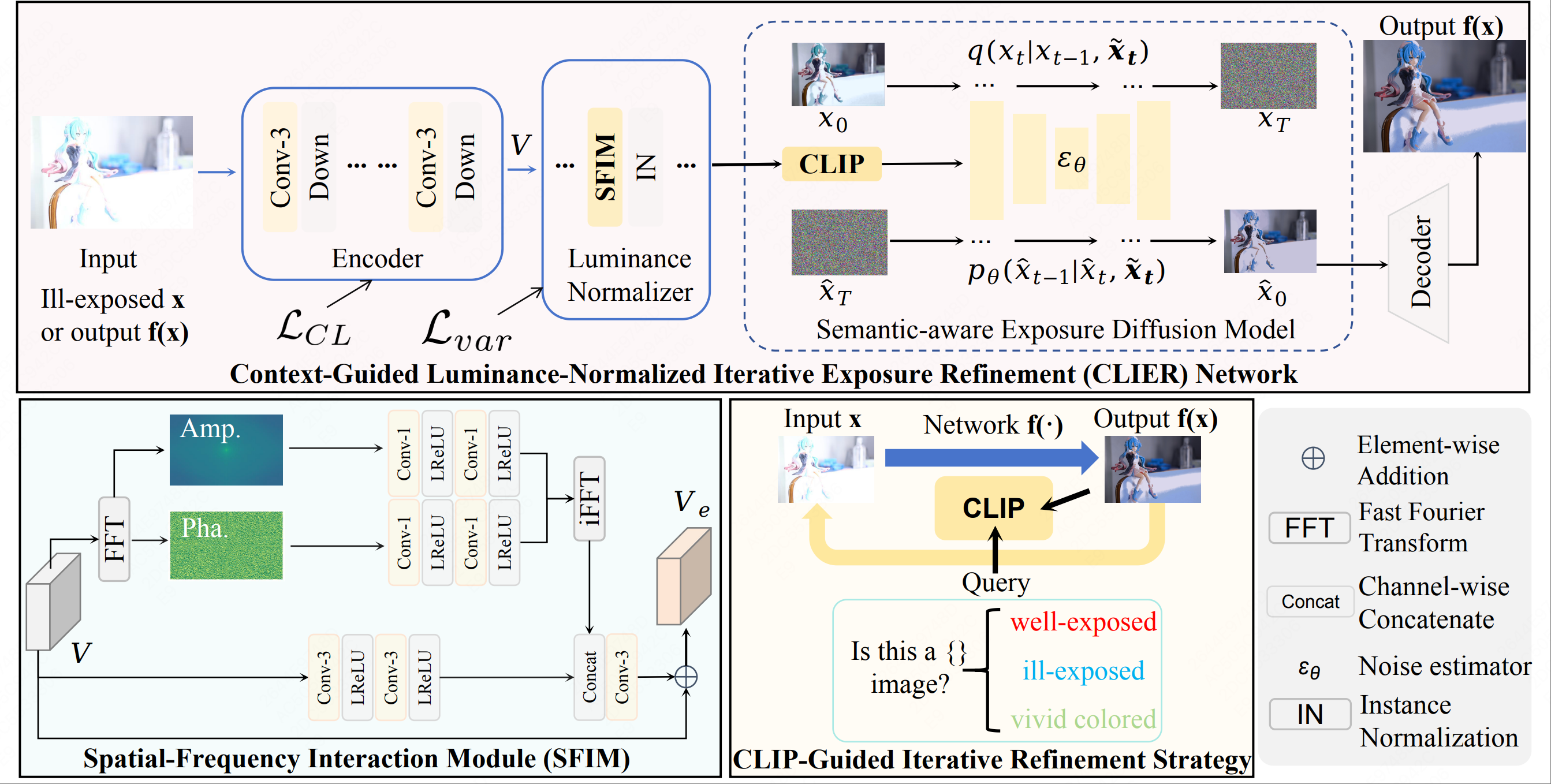
Exposure correction aims to restore over/under-exposed images to well-exposed ones using a single network. However, existing methods mainly handle non-extreme exposure conditions and struggle with the severe luminance and texture loss caused by extreme exposure. Through a thorough investigation, we find that the lack of high-quality benchmark datasets significantly limits progress in extreme exposure correction. To address this issue, we introduce the first Real-world Extreme Exposure Dataset, REED. By leveraging the burst shooting mode of cameras, we capture image sequences covering a luminance range from extremely dark to extremely bright. To prevent misalignment caused by camera motion and scene changes, we apply cropping and an improved SIFT algorithm to ensure precise alignment. We also propose a novel Context-Guided Luminance-Normalized Iterative Exposure Refinement Network. We employ Contrastive Loss and Luminance Normalizer to disentangle the coupled distribution of over/under-exposed images. In certain cases, luminance alone is insufficient for determining over/under-exposure, so we integrate semantic guidance into the Semantic-aware Exposure Diffusion Model to further enhance luminance and texture restoration. Inspired by the effectiveness of iterative correction in improving color and texture, we introduce the CLIP-Guided Iterative Refinement Strategy. Extensive experiments validate the superiority of our dataset and method. Our dataset and code will be publicly available.
Optical System to Collect Dataset
Network Architecture
@inproceedings{wangFromAbyssalICCV2025,
title = {From Abyssal Darkness to Blinding Glare: A Benchmark on Extreme Exposure Correction in Real World},
author = {Wang, Bo and Fu, Huiyuan and Huang, Zhiye and Zhang, Siru and Wang, Xin and Ma, Huadong},
booktitle = {Proceedings of IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision},
year = {2025}
}
